Discover how brain memory & learning work together to shape intelligence, habits, and success. Learn practical techniques to boost memory and speed up learning.
Brain Memory & Learning are two of the most fascinating abilities that define us as humans. Think about this: when you learned to ride a bicycle, you probably fell a few times. But eventually, your brain stored that skill so deeply that today you can ride without even thinking about it.
That is the magical connection between memory and learning—one allows you to capture knowledge, the other helps you apply it. Together, they form the foundation of education, creativity, innovation, and success.
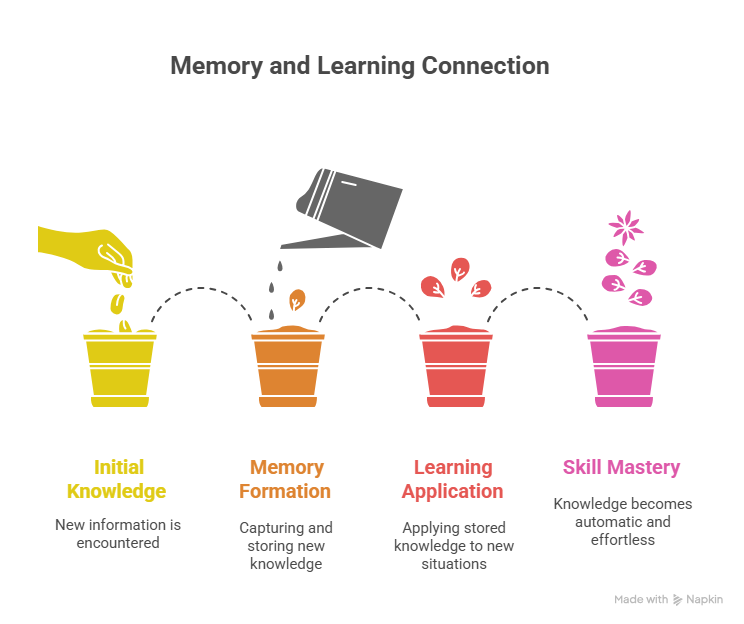
What is Brain Memory & Learning?
- Memory is the brain’s ability to store, retain, and recall information.
- Learning is the process of acquiring new knowledge, skills, and behaviors.
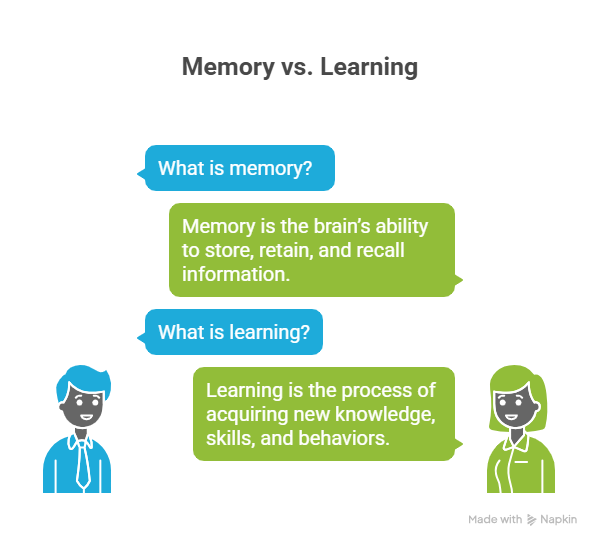
Without memory, learning would be impossible. And without learning, memory would be empty. They are like two sides of the same coin.
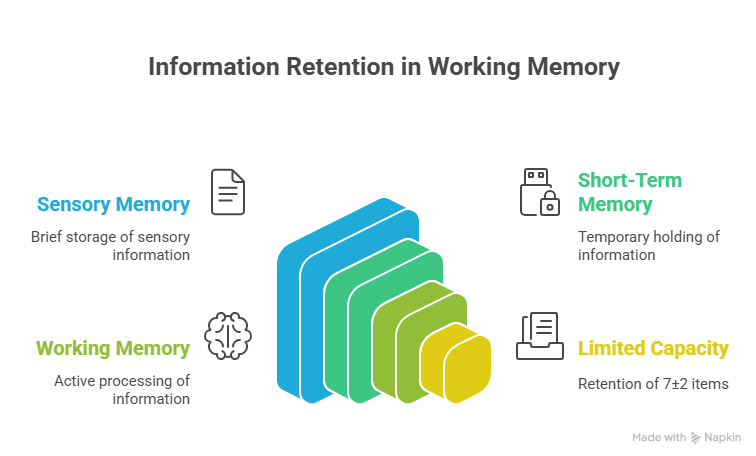
Types of Memory in the Brain
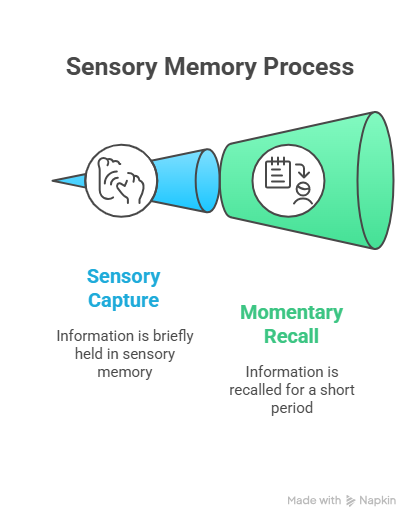
Sensory Memory
This is the first stage of memory. It captures information from your senses for a few seconds. For example, when you glance at a phone number and recall it for a moment, that’s sensory memory.
Short-Term Memory
Also known as working memory, this is where you hold information temporarily. For instance, remembering the items you need while shopping. But it’s limited—usually only 7±2 items.
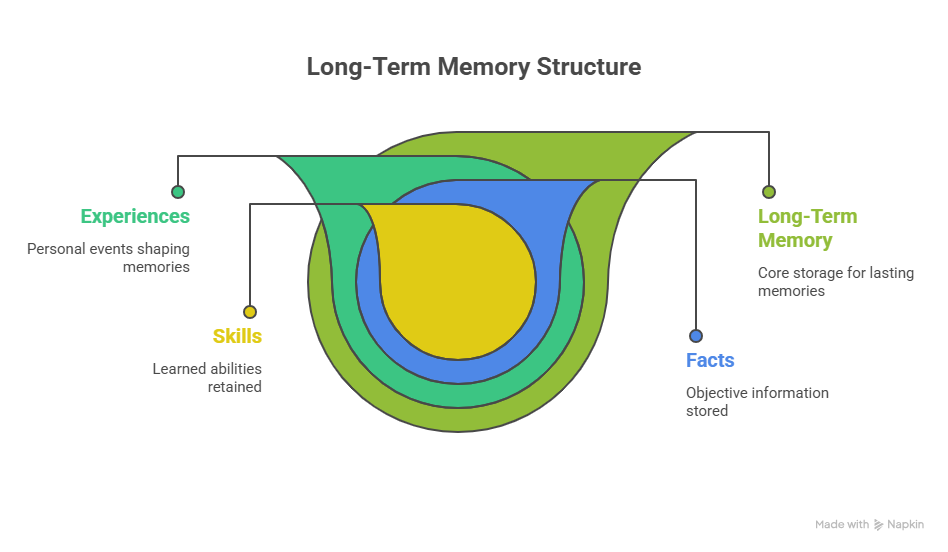
Long-Term Memory
This is where experiences, facts, and skills are stored for years or even a lifetime. Examples include remembering your childhood home or the ability to drive a car.
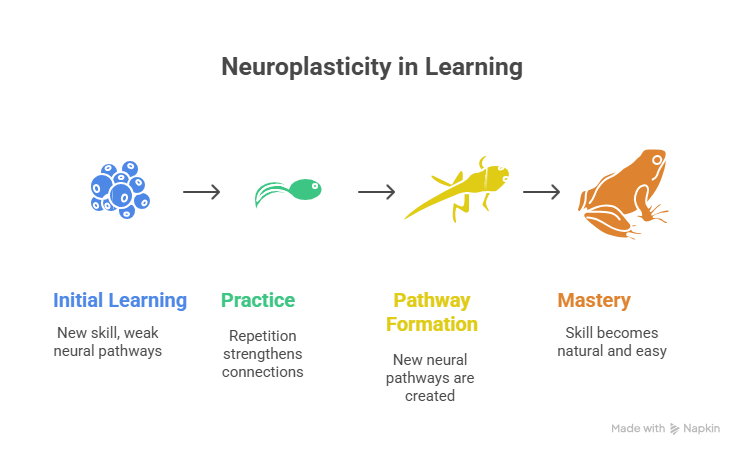
4. How Learning Happens in the Brain
Learning happens through neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to rewire itself by creating new neural connections. Each time you practice something, the brain strengthens those connections, making it easier to recall and repeat.
For example, when you learn a new language, neurons in your brain create new pathways. With practice, those pathways become stronger, and speaking the language becomes natural.
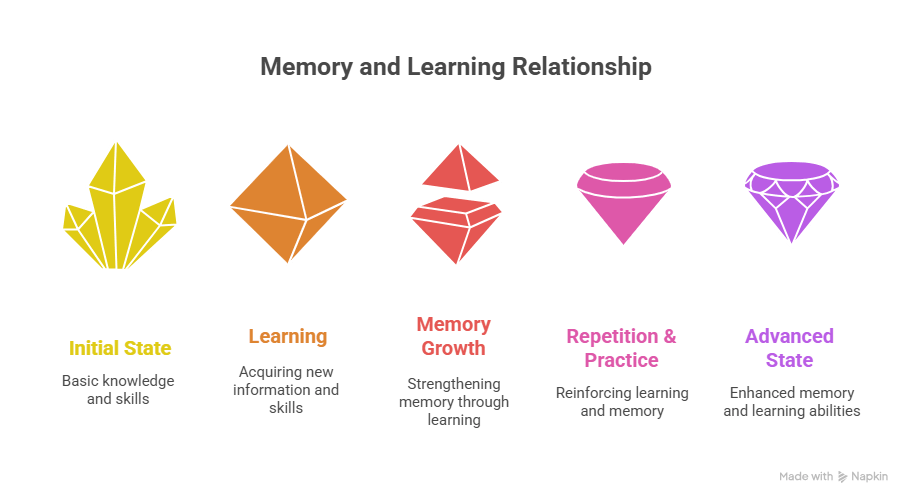
5. Connection Between Memory and Learning
- Learning builds on memory: You cannot solve advanced math if you don’t remember basic math.
- Memory grows through learning: Every new skill strengthens your memory.
- Both depend on repetition and practice.
A student preparing for exams depends heavily on both: memory for recalling facts, and learning for applying knowledge to problems.
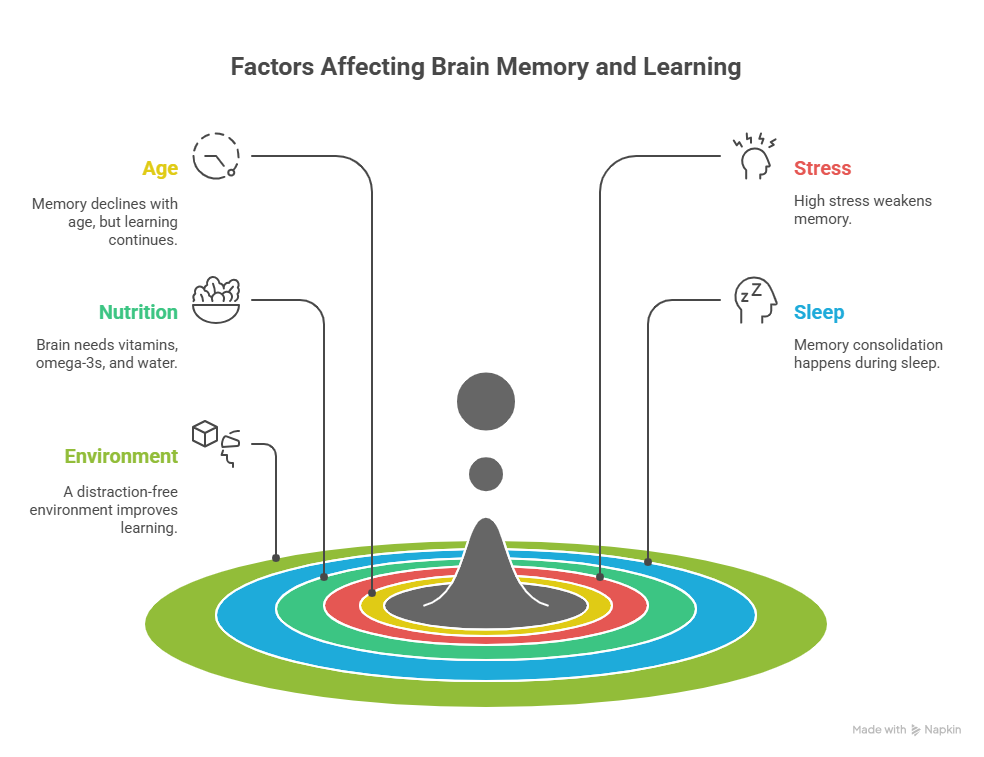
6. Factors That Affect Brain Memory & Learning
- Age – Memory declines with age, but learning never stops.
- Stress – High stress weakens memory.
- Nutrition – The brain needs vitamins, omega-3s, and water.
- Sleep – Memory consolidation happens during sleep.
- Environment – A distraction-free environment improves learning.
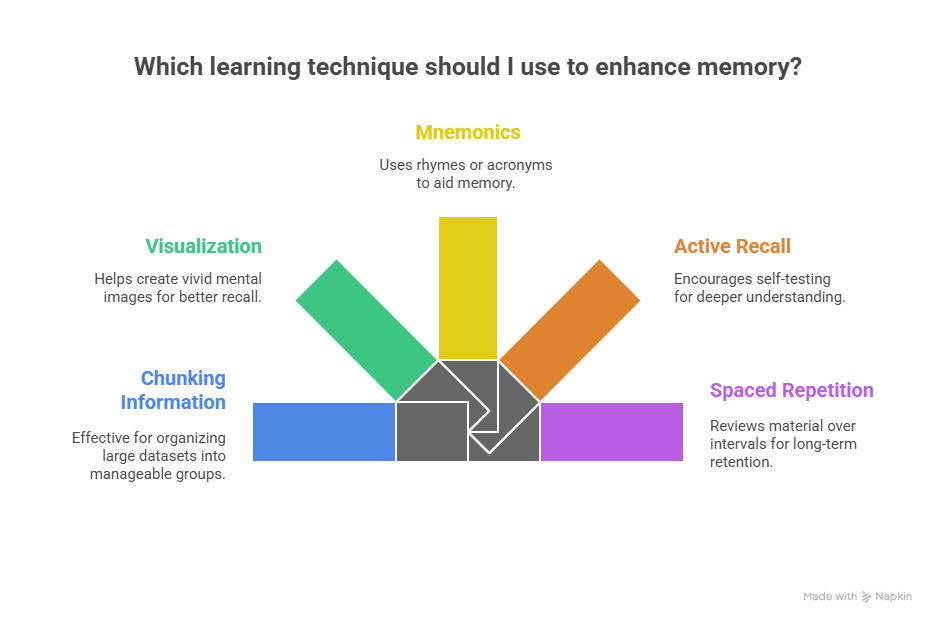
7. Techniques to Improve Memory Power
- Chunking Information – Break large data into small groups.
- Visualization – Turn words into images in your mind.
- Mnemonics – Use rhymes or acronyms for recall.
- Active Recall – Test yourself instead of just reading.
- Spaced Repetition – Review lessons over intervals (used by apps like Anki).
8. How to Learn Faster and Smarter
- Focus on understanding, not memorizing.
- Use the Pomodoro Technique: study for 25 minutes, rest for 5.
- Teach what you learn—explaining something to others strengthens memory.
- Apply the 80/20 Rule: focus on the 20% of material that gives 80% of results.

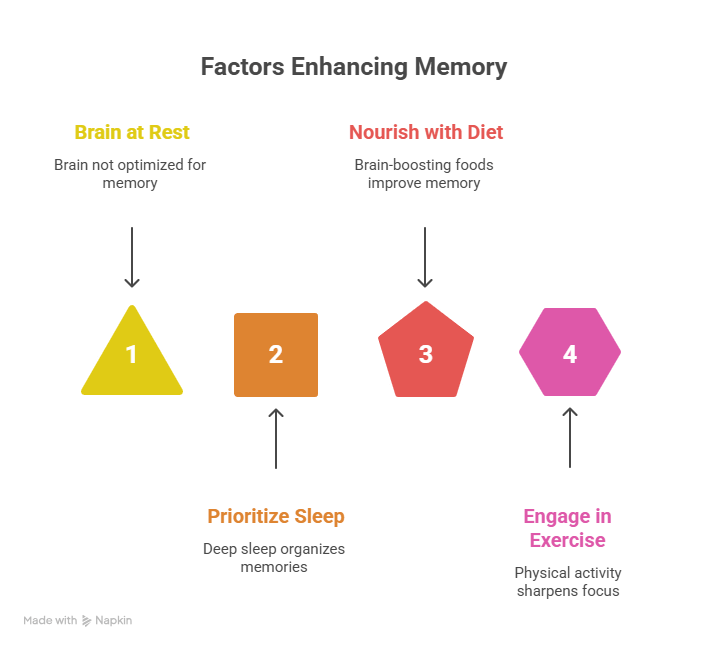
9. Role of Sleep, Diet, and Exercise in Memory & Learning
- Sleep: During deep sleep, your brain organizes and stores information.
- Diet: Foods like blueberries, nuts, and fish boost memory.
- Exercise: Physical activity increases oxygen to the brain, sharpening focus.
A healthy lifestyle is a natural brain booster.
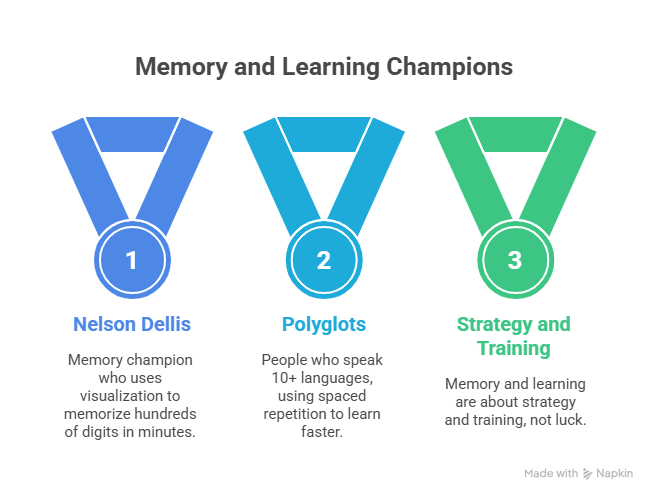
10. Real-Life Examples: Memory Champions and Learning Masters
- Nelson Dellis, a memory champion, can memorize hundreds of digits in minutes using visualization.
- Polyglots (people who speak 10+ languages) use spaced repetition to learn faster.
These examples prove that memory and learning are not about luck, but about strategy and training.
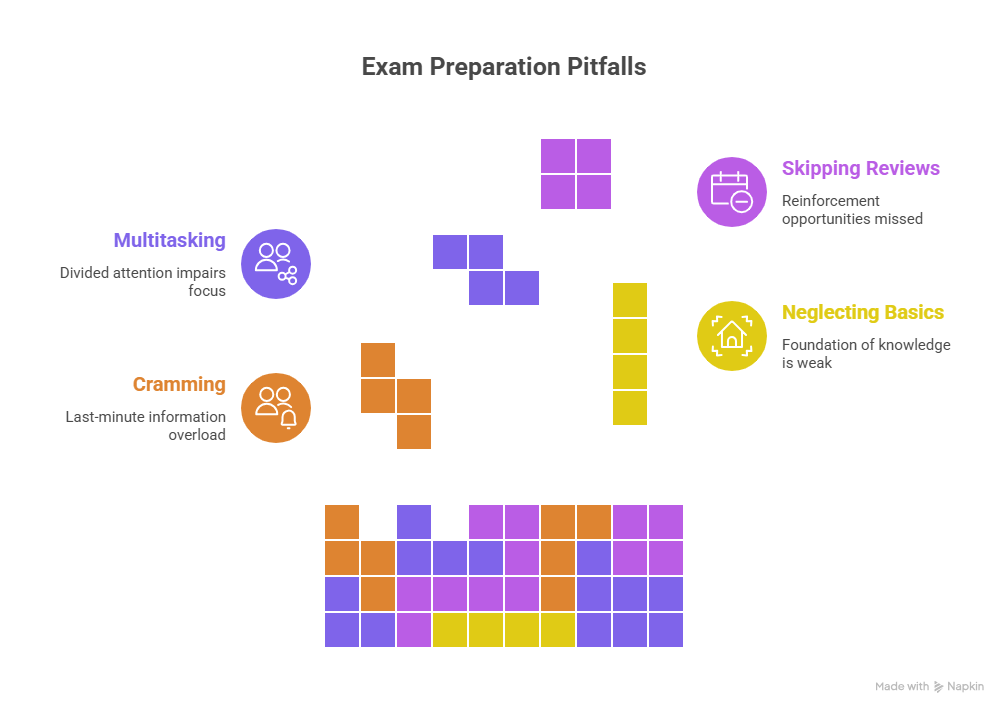
11. Mistakes People Make in Learning
- Cramming the night before exams.
- Studying without understanding the basics.
- Multitasking while learning (it divides focus).
- Ignoring review sessions.
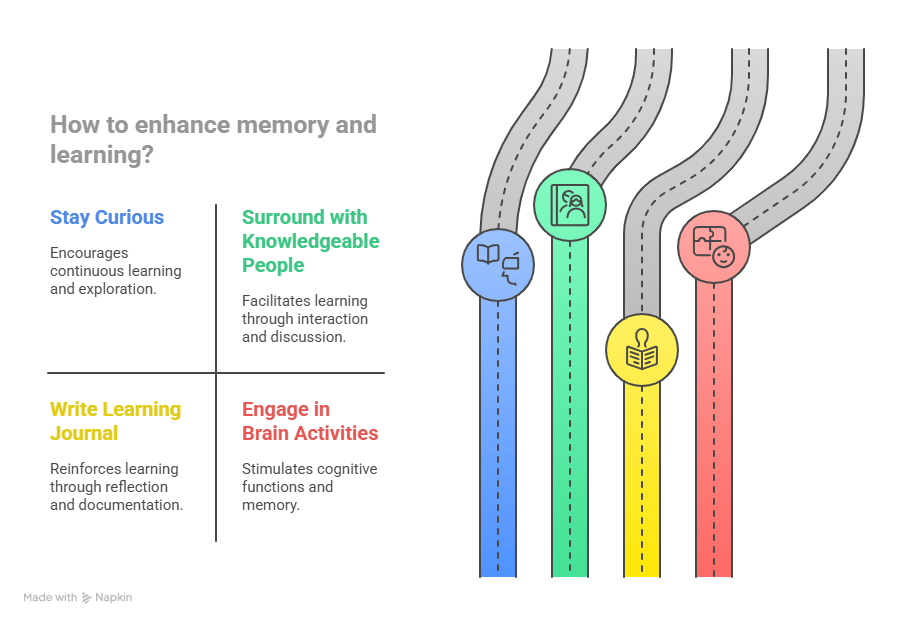
12. Science-Backed Tips for Lifelong Learning
- Stay curious and keep reading.
- Surround yourself with knowledgeable people.
- Write a daily learning journal.
- Keep your brain active with puzzles, chess, or coding.
Learning is not only for students—it is for every human being who wants to grow.
End of Summary
Brain Memory & Learning are not just academic concepts—they are the keys to personal and professional growth. By understanding how memory works and applying scientific learning strategies, anyone can unlock their full potential.
Think of your brain as a library: the more you care for it, the richer your collection of knowledge becomes.
So, take care of your memory, practice smart learning, and remember: your brain is capable of more than you think.


